Benzodiazepines
· Oral midazolam remains the mainstay
of anxiolytic premedication in children despite occasional unpredictable
effects.
· Elders are more sensitive to the
midazolam probably because of the
increased receptor binding affinity, impaired hemostatic mechanism and
higher sensitivity of the aged CNS
Mechanism of action
· As we know that benzodiazepines are
anxiolytics and anxiety is caused by the over stimulation of excitatory
neurotransmitters
· In order to reduce anxiety, seizures
and epilepsy we do use these class of
drugs as to increase the inhibitory activity
· Antidote for the overdose of the BZD
is flumazenil
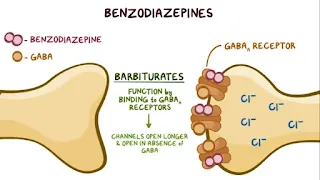
· BZD also binds to the gaba receptors
A but it bind to another site as do by gaba so they both enhances the inhibitory
effect and hence increase the influx of cl ions to inside the cell
· The imidazole provide its water
solubility at low pH
· As you can see in below picture
Overview of benzodiazepines
· Diazepam and lorazepam are well
absorbed from GIT with peak plasma concentration usually achieve in 1-2 hours
· IV midazolam dose is 0.05-0.1mg/kg
· Oral midozlam 0.25-1mg/kg
· All
BZD are highly protein bound about 90-98%
· Lorazepam and diazepam is used as antiepileptic
agents
· BZD used for acute insomnia
· It’s not recommended in chronic
insomnia because of dependence and tolerance effect of BZD
· In dose dependent fashion BZD
decreases the CMRo2 and CBF and hence decrease ICP
· It causes mild muscle relaxation
which may be good one but due to its muscle relaxation it can causes the airway
obstruction too so in premedication dose should be reduced
· It also cause the dose related
respiratory depression and ventilator response to co2 is impaired and hypoxic ventilator
responses are markedly depressed it’s because it don’t depress the oblongata
· That’s why patient with hypoventilation
syndromes and type 2 respiratory failure are more prone to the depression
· They have modest effect on the
hemodynamic effects though a decreases in SVR and hence arterial bp may occur
and so significant hypotension can occur in hypovolemic patients
· After intravenous bolus
administration, termination of action occurs largely by redistribution and
hepatic metabolism.
· Elimination takes place by hepatic
metabolism followed by renal excretion of the metabolites.
· Some of the benzodiazepines, including
diazepam, have active metabolites which greatly prolong their clinical effects.
Renal dysfunction results in the accumulation of these metabolites, and this is
an important factor in delayed recovery from prolonged sedation in the ICU.
· The half-life of diazepam is 20-70h
but its active metabolites like desmethyl diazepam have half-life of 36-200h
and also nor diazepam>100h
· Temazepam is the only orally available
drug its widely used as premedication because of its anxiolytic properties
· Oral absorption can take up to 2h for
peak concentration
· Elimination half-life is shorter than diazepam and is 8-15h and onset of
action more rapid and is 45-60min
· Tolerance and dependence less likely
occur that’s why advised as hypnotic agent
· Premedication dose is 10-20mg orally
60-120 min prep
· Lorazepam is drug of choice for
status epilepticus
· Also panic attacks
· Amnesia is marked feature of this
drug
|
Drug |
Features |
|
Temazepam |
Anxiolytic agent and only oral drug |
|
Lorazepam |
Status epileptics, panic attacks and marked one is amnesia |
|
Diazepam |
First BZD available |
|
Midazolam |
1.5-2 times more potent than diazepam and use short
term IV sedative |







0 Comments